Standards for Undergraduate Education
At the following sites, you will find relevant standards for School of Education educator candidates.
- MTTC (Michigan Test for Teacher Certification) Study Guides: Shows what material is covered on a subject area test and provides a look at a few sample questions
- Program Standards: Shows content standards for each specialty area program (major, minor) endorsed in Michigan, including those offered by Spring Arbor
- InTASC (Interstate Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium): The State of Michigan has ceded the creation of standards that should be addressed in all planned or professional education programs, both elementary and secondary, to this national consortium
- Common Core Standards | nationwide
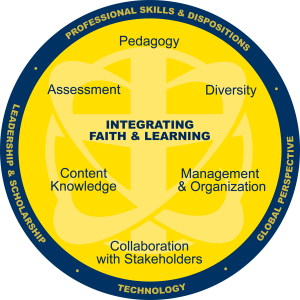
The School of Education utilizes our own Model of Teacher Education as a conceptual framework that undergirds our teacher preparation program. There is a central domain, Integrating Faith & Learning, that demonstrates the importance and impact the Spring Arbor Concept has on the School of Education and its programs. The core domains are in the inner circle, and the ones on the “outer” rim actually permeate all.
The SOE faculty describe each domain of the Model as follows:
- Integrating Faith and Learning enhances the development of professionally empowered educators who exhibit the principles of service to mankind with Christ as the model in personal and professional situations;
- Pedagogy, or the art and science of teaching, includes a repertoire of instructional strategies with learning (making meaning) as the central focus. Effective teachers have the ability to adapt learning to individual student needs through a variety of teaching methods;
- Assessment involves selecting, developing, and using appropriate strategies and instruments to measure achievement of program goals and instructional objectives. It includes an understanding of the effective use of different forms and timing of classroom assessment as an integral part of learning and teaching;
- Diversity encourages an understanding of how students differ in their approaches to learning and the need to create instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse populations. This domain recognizes the influence of culture, language, race, ethnicity, gender, religion, and cognitive and physical abilities on student learning; supports the learning of the exceptional child, and promotes development of an inclusive environment;
- Content Knowledge encompasses the theories, principles, and concepts of a particular discipline. This includes deep knowledge of the subject itself as well as an understanding of how that content is integrated and best taught across the curriculum;
- Management and Organization involves planning to maximize learning; organizing time, materials, equipment, and data to enhance academic performance; minimizing interruptions and behavioral problems; and motivating learners;
- Collaboration with Stakeholders involves building working relationships and communicating effectively with stakeholders (students, teachers and administrators, families, community members, etc.) to enhance learning; promoting effectiveness; advocating for change and developing practical strategies and processes through which people can effect change, solve problems and improve practices;
- Professional Dispositions and Skills are habits of thinking and action that emanate from professional attitudes, values, and beliefs. They are demonstrated through both verbal and non-verbal behaviors as educators interact with students, families, colleagues, and communities;
- Global Perspective enhances an awareness, understanding and appreciation of the world beyond oneself, one’s community, and one’s culture, as reflected in teachers’ choices and actions;
- Leadership and Scholarship includes the ability to provide exceptional guidance and direction as classroom teachers and in the larger educational arena through mentoring, service, and advocacy. This domain encourages an understanding of the value and role of scholarship and intellectual engagement to inform and enhance professional performance; and
- Technology, a universal tool in contemporary culture, calls for literacy, skill, and intent to appropriately use it in all aspects of effective teaching. Technology competency encompasses electronic media, hardware, software, and other devices and applications.
The Model connects to MI-INTASC per the following crosswalk:
| Model | MI-INTASC |
|---|---|
| Integration of Faith and Learning | (no specific correspondence, but related to Learner and Learning 2) |
| Pedagogy | Learner and Learning (1, 2, 3), Instructional Practice (7, 8) |
| Diversity | Learner and Learning (1, 2) |
| Management & Organization | Instructional Practice (7), Learner and Learning (1, 2, 3) |
| Collaboration with Stakeholders | Professional Responsibility (9, 10) |
| Content Knowledge | Content Knowledge (4, 5) |
| Assessment | Instructional Practice (6), Learner and Learning (3) |
| Professional Skills and Dispositions | Professional Responsibility (9, 10) |
| Global Perspective | Content Knowledge (5), Learner and Learning (2) |
| Technology | (infused throughout) |
| Leadership & Scholarship | Professional Responsibility (9, 10) |
Recent Comments